Maintaining your dog’s health and well-being begins with providing the right amount of nutrition. Just like humans, dogs need a balanced diet to thrive, and knowing how many calories your dog needs daily is crucial for their overall health. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of calculating your dog’s daily caloric needs, considering factors such as age, weight, activity level, and health status.
Understanding Caloric Needs
What are Calories?
Calories are units of energy. In the context of pet nutrition, calories refer to the energy that food provides to sustain your dog’s body functions, such as breathing, digestion, and physical activity.
Importance of Calculating Caloric Needs
Calculating your dog’s daily caloric needs helps you:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Prevents obesity and underweight conditions.
- Ensure Balanced Nutrition: Provides the necessary nutrients for growth, maintenance, and energy.
- Monitor Health: Helps in managing health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and joint issues.
Factors Influencing Caloric Needs
Age
- Puppies: Require more calories per pound of body weight than adult dogs due to their rapid growth and high energy levels.
- Adult Dogs: Caloric needs stabilize but vary based on activity level and metabolism.
- Senior Dogs: Often require fewer calories due to decreased activity levels and slower metabolism.
Weight
- Ideal Weight: Maintaining your dog’s ideal weight is crucial for overall health.
- Overweight or Underweight: Adjust caloric intake to help achieve a healthy weight.
Activity Level
- Sedentary Dogs: Dogs with minimal physical activity need fewer calories.
- Moderately Active Dogs: Regular exercise increases caloric needs.
- Highly Active Dogs: Dogs involved in intense activities like agility training or herding require more calories.
Health Status
- Spayed/Neutered Dogs: Tend to have lower caloric needs due to reduced metabolism.
- Pregnant/Lactating Dogs: Require additional calories to support their increased energy demands.
- Health Conditions: Certain health conditions may affect caloric needs, such as hypothyroidism (lower needs) or hyperthyroidism (higher needs).
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Your Dog’s Daily Caloric Needs
Step 1: Determine Your Dog’s Resting Energy Requirement (RER)
Resting Energy Requirement (RER) is the number of calories your dog needs at rest to maintain basic body functions. The formula to calculate RER is:
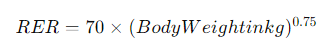
Example Calculation
For a dog weighing 10 kg:
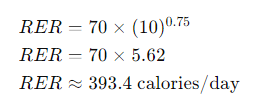
Step 2: Determine Your Dog’s Maintenance Energy Requirement (MER)
Maintenance Energy Requirement (MER) accounts for additional calories needed based on activity level, age, and other factors. Use the following multipliers based on your dog’s status:
- Puppies (0-4 months): RER x 3
- Puppies (4 months-1 year): RER x 2
- Adult, Neutered Dogs: RER x 1.6
- Adult, Intact Dogs: RER x 1.8
- Inactive/Senior Dogs: RER x 1.2
- Active Dogs: RER x 2
- Highly Active Dogs: RER x 3
- Pregnant Dogs: RER x 2
- Lactating Dogs: RER x 4-8 (depending on the number of puppies)
Example Calculation
For a neutered adult dog weighing 10 kg:
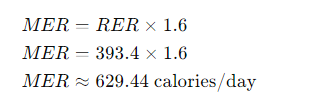
Step 3: Adjust for Individual Needs
Consider individual variations such as metabolism, breed-specific needs, and overall health. Monitor your dog’s weight and adjust caloric intake as needed.
Step 4: Measure Food Accurately
Use a kitchen scale to measure your dog’s food accurately, ensuring they receive the correct amount of calories daily.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Dog’s Diet
Regular Weigh-Ins
- Weekly Weigh-Ins: Weigh your dog weekly to monitor weight changes.
- Adjust Caloric Intake: Increase or decrease caloric intake based on weight gain or loss.
Observing Body Condition
Use a body condition score (BCS) chart to assess your dog’s body condition visually. Adjust feeding amounts based on whether your dog is underweight, overweight, or at an ideal weight.
Consulting Your Veterinarian
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor your dog’s health and adjust their diet as needed.
- Professional Guidance: Consult your veterinarian for personalized advice based on your dog’s specific needs and health conditions.
Tools and Resources for Calculating Caloric Needs
Online Caloric Calculators
Many websites and pet care apps offer online calculators to help determine your dog’s daily caloric needs based on their weight, age, and activity level.
Pet Nutrition Labels
Check the nutrition labels on commercial dog foods to determine the caloric content per serving. Adjust the amount you feed your dog based on their daily caloric needs.
Veterinary Resources
- Professional Advice: Consult your veterinarian or a veterinary nutritionist for accurate caloric calculations and diet recommendations.
- Educational Materials: Use educational materials and resources provided by veterinary clinics and pet nutrition experts.
Common Questions About Dog Caloric Needs
How Often Should I Feed My Dog?
The number of meals per day can vary based on age, size, and health:
- Puppies: 3-4 meals per day.
- Adult Dogs: 2 meals per day.
- Senior Dogs: 2 meals per day, or as recommended by your veterinarian.
Can I Feed My Dog Human Food?
While some human foods are safe for dogs, many are not. Always consult your veterinarian before introducing human food to your dog’s diet.
How Can I Tell If My Dog Is Getting Enough Calories?
Signs your dog is getting enough calories include:
- Healthy Weight: Maintaining an ideal weight and body condition.
- Energy Levels: Consistent energy and activity levels.
- Healthy Coat: A shiny, healthy coat.
What Should I Do If My Dog Is Overweight?
If your dog is overweight:
- Consult Your Veterinarian: Seek professional advice on a weight management plan.
- Adjust Caloric Intake: Reduce daily caloric intake gradually.
- Increase Activity: Incorporate more physical activity into your dog’s routine.
What Are the Risks of Overfeeding or Underfeeding?
Overfeeding can lead to obesity, which increases the risk of health issues such as diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems. Underfeeding can result in malnutrition, weakened immune system, and decreased energy levels.
Special Considerations for Different Dog Breeds
Small Breeds
Small breeds have faster metabolisms and higher energy needs per pound of body weight compared to larger breeds. Ensure their caloric intake meets their high energy demands.
Large Breeds
Large breeds are prone to joint issues and obesity. Monitor their weight closely and adjust caloric intake to prevent excessive weight gain.
Working Breeds
Working breeds such as herding dogs, sled dogs, and hunting dogs have higher energy needs due to their physical activities. Provide sufficient calories to support their active lifestyle.
Conclusion
Calculating your dog’s daily caloric needs is essential for maintaining their health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence caloric requirements and following a step-by-step approach, you can ensure your dog receives the right amount of nutrition to thrive. Regular monitoring, adjustments, and consultation with your veterinarian will help you provide the best care for your furry friend.
FAQs
How often should I recalculate my dog’s caloric needs?
Recalculate your dog’s caloric needs periodically, especially if there are changes in their weight, activity level, or health status. Regular veterinary check-ups can help determine when adjustments are needed.
Can I use treats in my dog’s daily caloric intake?
Yes, include treats in your dog’s daily caloric intake to prevent overfeeding. Ensure treats make up no more than 10% of their total daily calories.
What if my dog has a specific health condition affecting their caloric needs?
Consult your veterinarian for personalized dietary recommendations if your dog has a health condition that affects their caloric needs, such as diabetes, thyroid issues, or obesity.
Are there breed-specific guidelines for calculating caloric needs?
While general guidelines apply to all dogs, some breeds have unique nutritional requirements. Consult your veterinarian or a veterinary nutritionist for breed-specific advice.
Can I switch my dog’s diet without affecting their caloric needs?
When switching your dog’s diet, do so gradually over 7-10 days to prevent digestive issues. Monitor their weight and adjust caloric intake as needed to ensure they receive the right amount of calories from the new diet.


